외부 설정
외부 설정을 정의할 수 있는 위치는 기본적으로 다음과 같다.
- src/main/resources/application.properties
- src/main/resources/application.yml
- 환경 변수
- command line arguments
아래 코드로 테스트 결과를 확인할 수 있다.
package com.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SampleRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Value("${custom.name}")
private String name;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("=================================");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println("=================================");
}
}
# src/main/resources/application.yml
custom:
name: test
실행 결과
2020-04-20 11:29:57.703 INFO 3188 --- [ main] com.example.Application : Started Application in 1.62 seconds (JVM running for 2.141)
=================================
test
=================================
우선 순위
우선 순위는 굉장히 많은 단계가 있다.
- 유저 홈 디렉토리에 있는 spring-boot-dev-tools.properties
- 테스트에 있는 @TestPropertySource
- @SpringBootTest 애노테이션의 properties 애트리뷰트
- 커맨드 라인 아규먼트
- SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON (환경 변수 또는 시스템 프로티) 에 들어있는 프로퍼티
- ServletConfig 파라미터
- ServletContext 파라미터
- java:comp/env JNDI 애트리뷰트
- System.getProperties() 자바 시스템 프로퍼티
- OS 환경 변수
- RandomValuePropertySource
- JAR 밖에 있는 특정 프로파일용 application properties
- JAR 안에 있는 특정 프로파일용 application properties
- JAR 밖에 있는 application properties
- JAR 안에 있는 application properties
- @PropertySource
- 기본 프로퍼티 (SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties)
따라서 위의 예제는 15 순위 JAR 안에 있는 application properties를 사용한 것이다.
테스트 케이스용 외부 설정도 정의할 수 있다. src/test/application.{yml, properties}에 정의하면 테스트 진행시 해당 파일을 resources에 정의된 application.{yml, properites} 무시하고 로드한다.
다음 테스트를 보면 그 차이를 확인 할 수 있다.
package com.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SampleRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Value("${custom.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${custom.age}")
private int age;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("=================================");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println("=================================");
}
}
# src/main/resources/application.yml
custom:
name: test
age: ${random.int} # 랜덤 값 지정
실행 결과
2020-04-20 12:07:42.766 INFO 5853 --- [ main] com.example.Application : Started Application in 1.38 seconds (JVM running for 1.878)
=================================
test
1063398586
=================================
무사히 실행 된다.
테스트 설정
테스트 케이스는 어떨까? 아래와 같이 테스트 케이스를 만들어 테스트를 진행한다.
package com.example;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SampleRunnerTest {
@Autowired
Environment env;
@Test
public void testRun() throws Exception {
assertThat(env.getProperty("custom.name"))
.isEqualTo("test");
}
}
# src/test/resources/application.yml
custom:
name: test
이제 테스트를 진행하면 테스트가 실패함을 볼수 있다. 에러 로그를 보면 다음과 같이 age 속성을 확인 할 수 없다고 나온다.
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'sampleRunner': Injection of autowired dependencies failed; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Could not resolve placeholder 'custom.age' in value "${custom.age}"
이는 test의 설정에도 같은 속성을 정의하면 해결되지만, 이후에 어떤 속성이 추가될 지 모르기 때문에 별도의 파일로 관리 하는 것을 권장한다. 또한 @PropertySoruce는 yml 파일을 지원하지 않다 하니 .properties 로 변경할 것을 권장한다.
# src/main/resources/application.properties
custom.name=app
custom.age=${random.int} # 랜덤 값 지정
# src/test/resources/test.properties
custom.name=test
package com.example;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@TestPropertySource(locations = "classpath:/test.properties")
@SpringBootTest
public class SampleRunnerTest {
@Autowired
Environment env;
@Test
public void testRun () throws Exception {
assertThat(env.getProperty("custom.name"))
.isEqualTo("test");
}
}
위 테스트 케이스를 실행하면 통과할 것이고, 이전의 SampleRunner를 통해 표시되는 내용도 달라진 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
2020-04-20 14:11:55.186 INFO 11797 --- [ main] com.example.SampleRunnerTest : Started SampleRunnerTest in 1.74 seconds (JVM running for 2.491)
=================================
test
-994668283
=================================
src/main/resources/application.properties의 내용에 custom.name 을 app으로 변경했음에도 불구하고, 표시되는 내용은 src/test/resources/test.properties의 내용이 사용되었다. 이는 우선순위가 더 높은 설정(2순위의 @TestPropertySource)이 낮은 우선 순위의 설정(15순위의 JAR 안의 application.properties)를 덮어 쓰며 생긴 현상이다. 이전의 덮어쓰기와의 차이점은 설정 파일 자체를 교체한 것이 아닌, 파일 내용을 보며 키값을 비교해, 더 높은 우선 순위의 것을 사용한 점이다.
파일이 application.properties로 같은 경우에는 어떻게 될까?
우선순위는 다음과 같다.
- file:./config/
- file:./
- classpath:./config/
- classpath:./
file:./은 현재 프로젝트의 루트 디렉토리를 의미한다.
즉 src/main/resources/application.properties는 4순위의 우선순위를 갖는다.
타입 세이프 프로퍼티 @ConfigurationProperties
property 들을 Bean으로 등록 할 수 있다.
아래 의존성을 추가하면 내 프로젝트의 커스텀 설정의 메타데이터를 만들 수 있다. 예를 들면, IDE에서 properties 작성중 자동 완성의 정보를 만들 수 있다.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("custom")
public class CustomProperties {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
이렇게 빈(Bean)으로 등록한 Property를 사용하기 위해 SampleRunner도 변경한다.
package com.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SampleRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
CustomProperties custom;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("=================================");
System.out.println(custom.getName());
System.out.println(custom.getAge());
System.out.println("=================================");
}
}
이후 실행하면 정상적으로 설정 내용이 표시 될 것이다.
추가로, configuration processor를 추가한 결과도 다음과 같다.
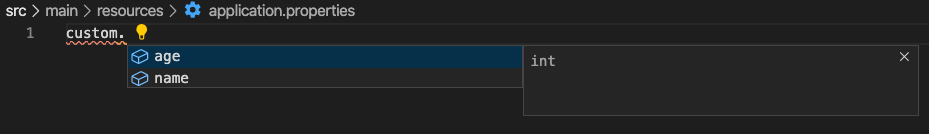 내가 만든 커스텀 설정이 자동완성을 지원하게 되었다.
내가 만든 커스텀 설정이 자동완성을 지원하게 되었다.
이 방식으로 설정을 적용할 경우 key의 case문제가 해결된다. camelCase, kebap-case 등 모두 자동으로 적용된다.
또한 타입 컨버젼도 지원한다.
package com.example;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DurationUnit;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("custom")
public class CustomProperties {
private String name;
private int age;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS)
private Duration duration;
public Duration getDuration() {
return this.duration;
}
public void setDuration(Duration duration) {
this.duration = duration;
};
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
이렇게 @DurationUnit을 사용해 Duration 타입으로 자동으로 변경된다. 또 @DurationUnit을 사용하지 않고도, properties 정의 시에 값에 s, ns 등으로 시간을 알수 있는 접미사를 붙이면 자동으로 변경된다.
프로퍼티 값 검증도 지원한다.
@Validated, 또는 JSR-303(@NotNull, ...)을 모두 지원한다.
